The latest update to our network inventory system, NetStork, brings significant leap in infrastructure development process, optimizing infrastructure and fiber optic routing, and introducing service modeling capabilities. Delve deeper into our article to uncover the full scope of what’s new and improved.
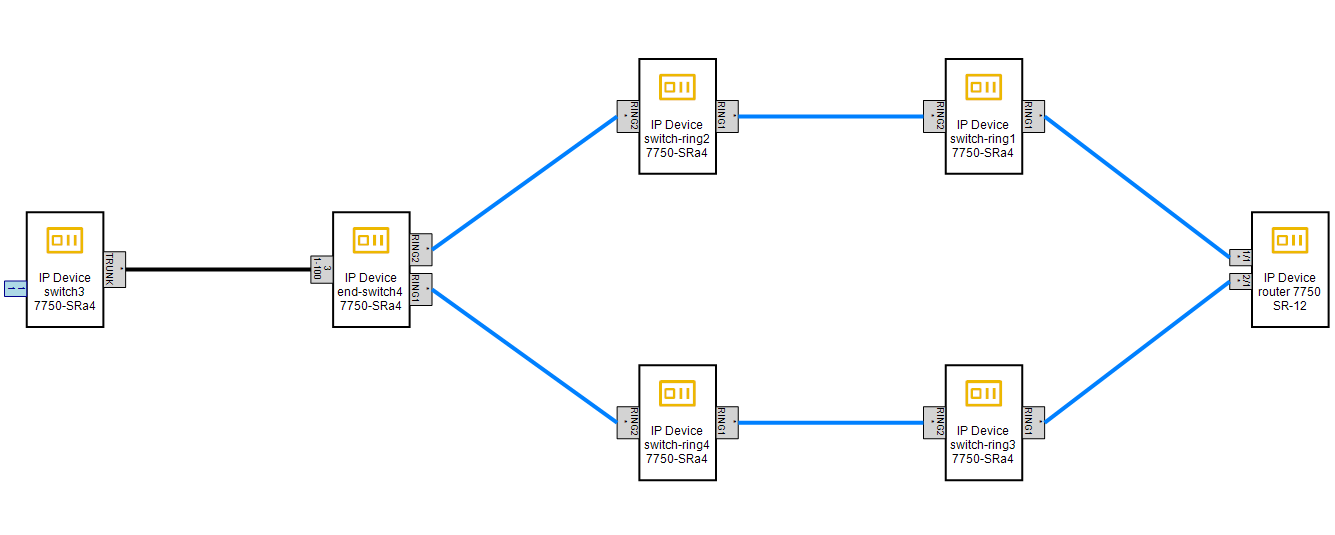
Building routes within the infrastructure and fiber optic routes
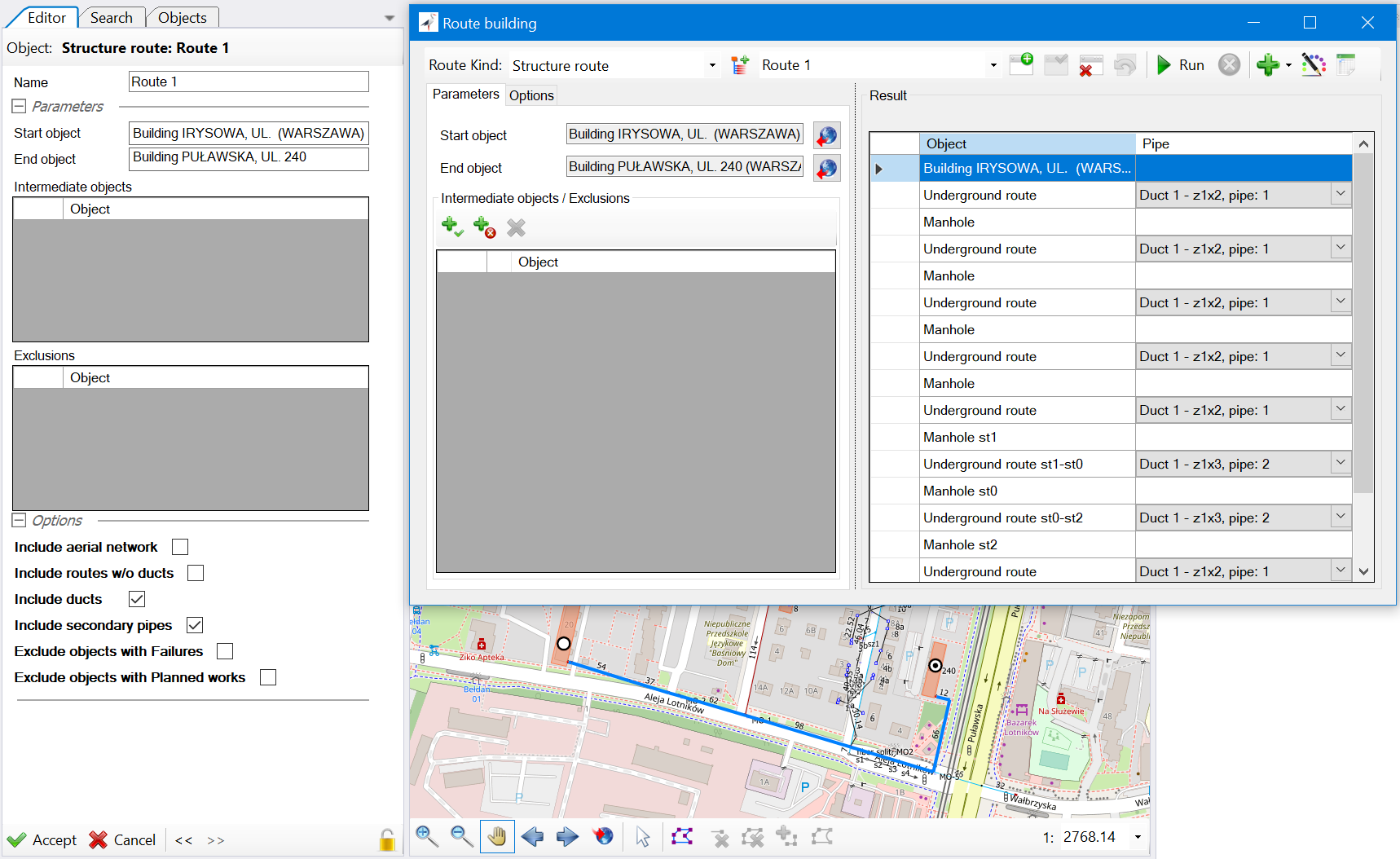
In NetStork 14, we’ve introduced a tool tailored for rapid route planning within network infrastructure and fiber optic networks. This feature empowers users to swiftly identify the shortest path from point A to point B. It also offers flexibility to incorporate multiple waypoints and exceptions, allowing users to customize routes to individual specifications. Moreover, users can automatically avoid certain events, such as outages or planned maintenance works.
The tool can save route calculation parameters as Route objects in the database. This facilitates the design of routes with the option to update them in the future based on the latest data and network conditions.
Users can further refine their routes by changing the destination pipes (primary/secondary) for each segment of the route. In the case of fiber optic routes, you can select individual fibers along the route.
Based on the designed infrastructure route in canalization, with just a single click, users can generate:
- a fiber optic cable,
- a secondary pipe/micro-canalization,
- a reservation of space in canalization,
- a canalization lease service.
Based on the fiber optic route, users can create:
- a dark fiber lease service,
- an Ethernet transmission service.
The tool also provides the following features:
- set up or modify existing cable routes,
- work simultaneously on multiple routes/route variants and switch between them using a drop-down list,
- export route data to CSV files,
- change route-finding options to fulfill specific requirements, whether it involves defining preferred types of network and pipes, minimizing the number of welds along the route, etc.
Service modeling
In NetStork 14, we’ve introduced the option to inventory the following services:
Canalization Lease Service
This service offers modeling capabilities for two types of services: leasing a route within a cable ducting system in the form of a secondary pipe chain and leasing a space in a cable ducting system as a pipe of any diameter.
The route of the canalization lease service can be built using the route building tool and/or modified manually. It is visualized as a service diagram and on the cross-section schemas as a striped circle.
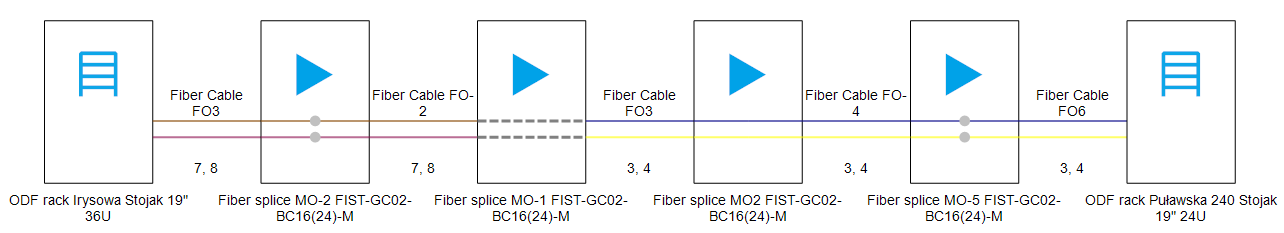
Dark Fiber Lease Service
The dark fiber lease service is based on a fiber relation object. It can be created from any fiber relation using context operation or using the route building tool and/or modified manually.
The route of a dark fiber lease service is visualized as a diagram that shows leased fibers and their connections, or the lack of connections if the service isn’t completed and fibers aren’t crossed between patch panels. Additionally, contextual operation can be used to automatically cross fibers.
Ethernet Data Transmission/Internet Access Service
The Ethernet data transmission service is established on a router/switch port, serving as the client’s access point to the network. If a client is connected through a fiber optic cable, the service may also include a fiber relation.
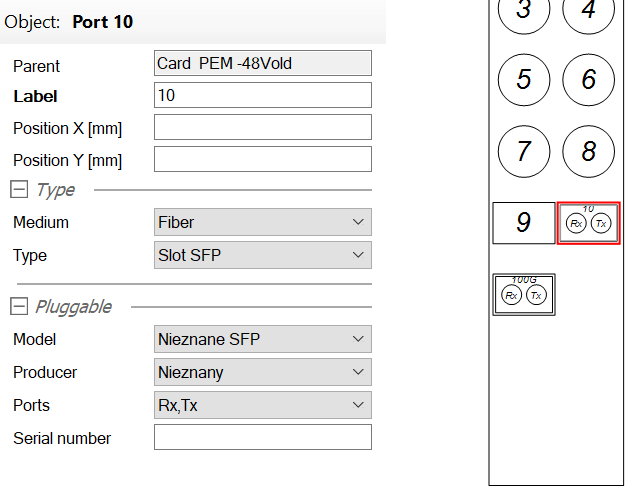
For the inventory of Internet Access services, we’ve introduced a modeling feature for SFP/XFP/CFP transceiver modules via a new port type: transceiver slot. This allows you to specify the type of installed transceiver for your port:
A VLAN connection diagram is introduced to visualize complex service transmissions in the network from the switch to the router. This new functionality enhances the management of Ethernet services.
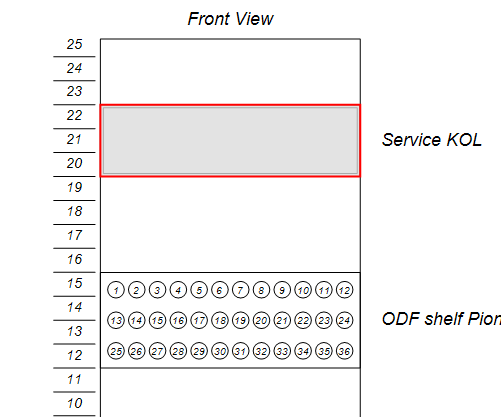
Colocation Service
The colocation service models the lease service of a place for a rack, or a space on a rack at the operator’s location. It’s visualized as a point geometry/area geometry on the building or level diagram, or as a rectangular area on the rack view diagram:
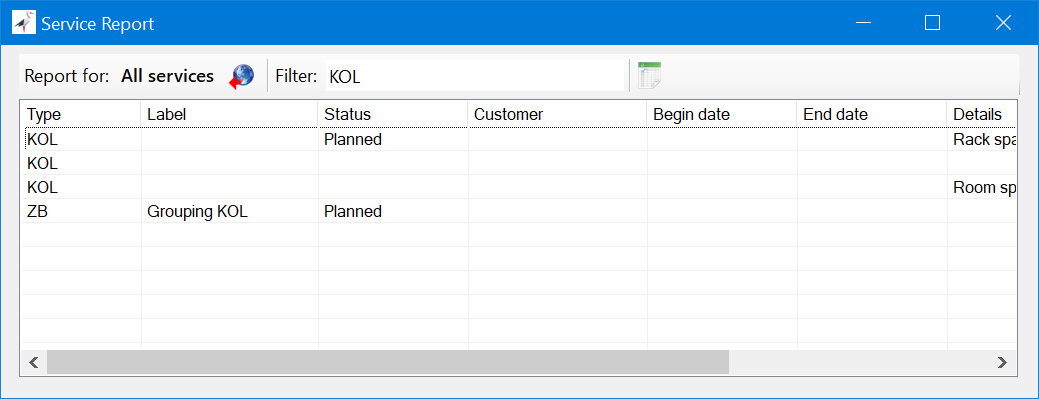
Service Search Tool
The service module includes a tool for fast service searching and reporting. The search engine allows users to:
- explore all services in the database,
- filter service list by keywords,
- display services related to a chosen object, e.g., any event or outage,
- navigate to a selected service in the application,
- export the current service list to a CSV file.
Combining Services into Packages
By leveraging the hierarchy of the Service object, users can group services into packages. This enables the inclusion of various secondary services within the grouping. Upon highlighting the grouping service, all secondary services are highlighted on a map.
Canalization modeling enhancements
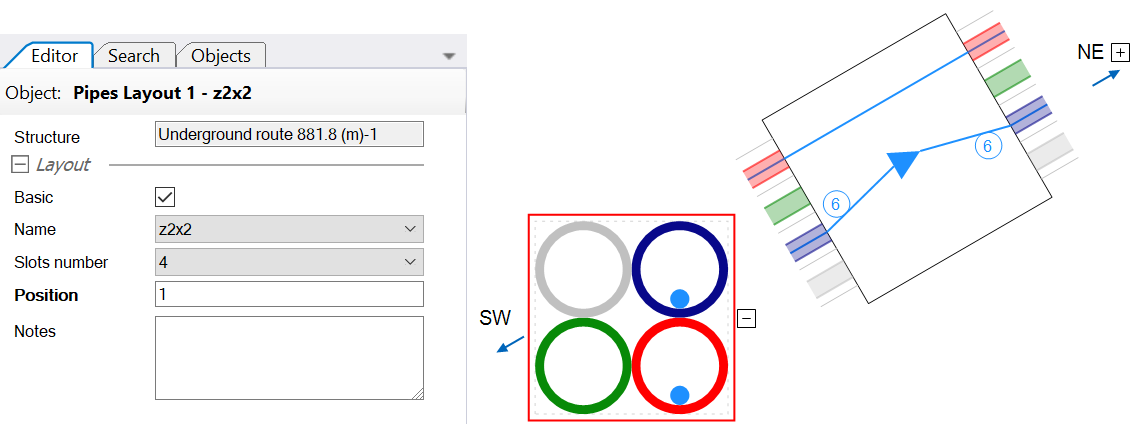
Secondary pipe layouts
Due to their cost-effectiveness, canalization increasingly utilizes secondary pipes made of synthetic materials laid directly in the ground. Consequently, there’s a growing demand to accurately visualize the placement of these pipes to ensure a better representation of reality in the field.
To address this requirement, we’ve introduced a function for entering secondary pipe layouts into the system, analogically to duct profiles and primary pipe layouts.
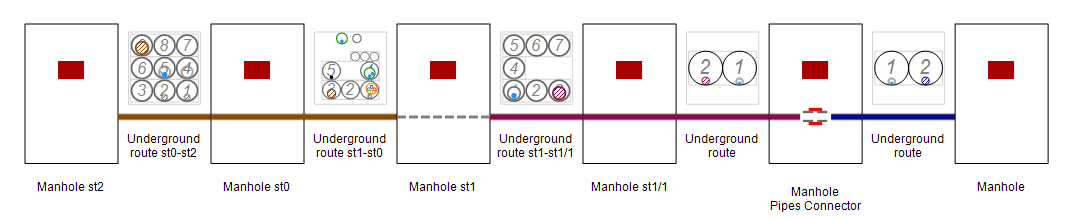
Modeling underground cable pits
Underground cable pits, frequently installed on secondary canalization as a cost-effective alternative to manholes, have been modelled in NetStork 14 using the Cable Hub object:
- We’ve incorporated essential attributes including Type, Production date, Owner, User, Technical condition, Physical status, and Origin.
- Additionally, NetStork 14 allows modeling scenarios where certain pipes bypass the underground cable pit, ensuring accurate representation by not drawing these cables on the location diagram.
Pipe thickness visualizations
We’ve introduced representations of pipe thickness on cross-sectional diagrams of underground routes. This enhancement allows users to enter pipe thickness directly by editing the pipe dictionary.
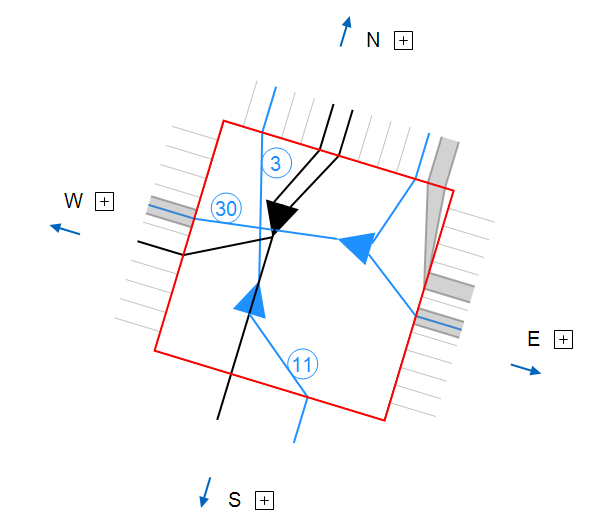
Navigation arrows on location diagrams
Arrows facilitate swift movement to the next location in the direction they indicate.
Navigation arrows on diagrams
Both structure and cable diagrams now feature navigation arrow buttons:
They serve two purposes:
- Facilitating seamless navigation to previously displayed diagrams.
- Swiftly switching to the object’s dedicated diagram after highlighting it on the current diagram. For example, clicking on a rack in a building’s diagram activates the arrow Show the next/new diagram, enabling users to display the rack view diagram.
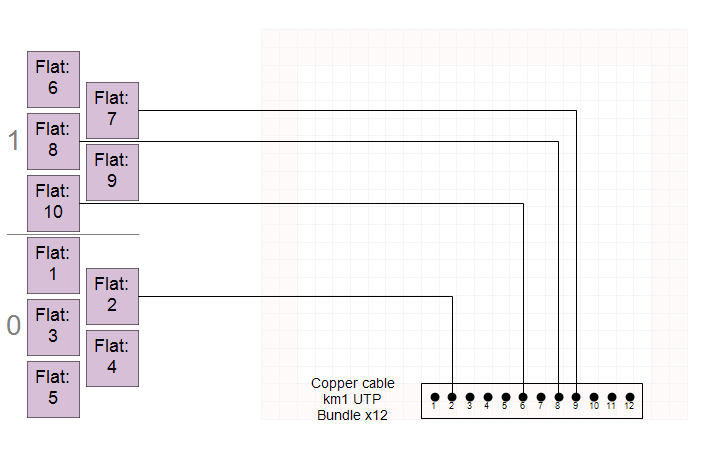
Connecting flats using the Ethernet technology
NetStork 14 introduces the capability to connect flats to the Ethernet twisted-pair cabling, mirroring the process of connecting to fibers in FTTH technology. This expansion enables modeling situations where the router/switch is not physically located within the same building as the connected flats. Unlike previous versions of NetStork, where the switch had to be placed in the same building to model such connections, this update broadens the scope of connectivity options.
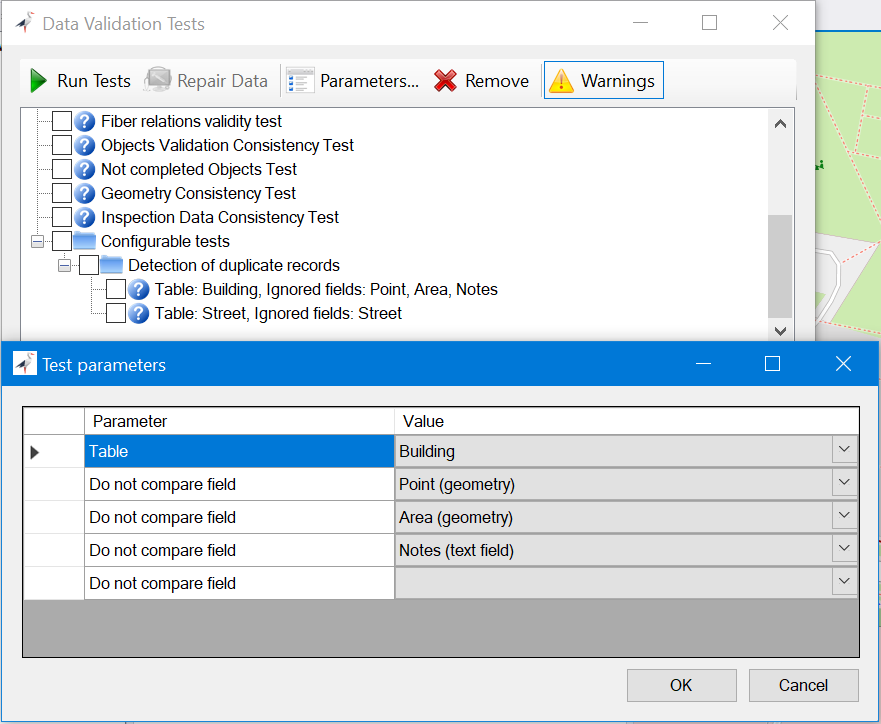
Detecting and deleting duplicates
Over time, accumulation of object duplicates may occur, where multiple records represent the same entity. To address this issue, we’ve introduced new diagnostic tools for detecting and deleting object duplicates. Users have the flexibility to configure custom tests to identify duplicates in any table (including dictionary tables), and selected attribute sets. Detected object duplicates can be viewed and merged in bulk, ensuring database consistency with consolidated, singular object units.
CSV loader enhancements
The CSV loader now offers expanded functionalities, including:
- Using expressions for initial data processing (creating artificial columns, combining existing columns, inserting default values, etc.).
- Loading different tables from the same file (multiple mapping of the same file).
- Defining conditions for loaded data to load only a subset of rows. For example, loading data from one file to multiple tables based on a column indicating the type of data.
- Commiting the import even in the presence of errors.
- Importing text data that include newline characters.
- Handling heterogeneous connections, such as setting cable end objects or rack parent objects.
- Exporting validation error lists to CSV files.
Other improvements in NetStork 14
- Enhanced map navigation arrows that now feature unlimited history.
- Introduction of a new button in the map toolbar for switching to the current object.
- Improved go to the current geometry button, allowing presentation of the chosen geometry, rather than the entire object.
- Better highlighting of point objects achieved by adjusting the scale to approximately 1:1000 instead of maintaining the same scale.
- New function for navigating to given coordinates as an expansion to the fast-searching function.
- New button for switching to the current position in the NetStorkWEB application.
If you’re contemplating acquiring a network inventory system or seeking to explore NetStork’s capabilities, we’re here to help! Whether you’re new to NetStork or considering upgrading to NetStork 14, feel free to reach out to us for more information.